physiologic tooth mobility
Should you be able to. Pathologic tooth mobility 1.

Carnivore Omnivore Herbivore Frugivore Human Spot The Differences Https Www Facebook Com Photo Php Fbid 7511411 Omnivore Carnivores Carnivore Teeth
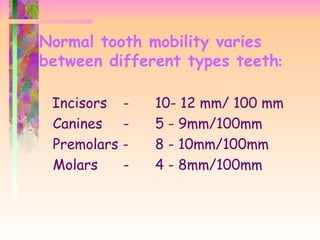
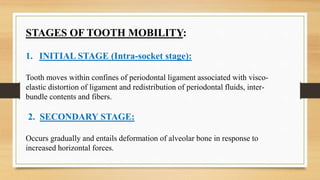
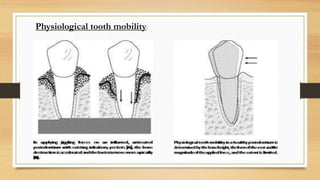
Physiologic tooth mobility it refers to moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue muhleman1951 korber1971 lindhe 1989 normal tooth mobility varies between different types teeth.

. PHYSIOLOGY OF TOOTH MOVEMENTS BY DR OYETOLA FEMI Deleterious effects of orthodontic tooth movements Mobility and pain Effect on the pulp pulpitis Root. This mobility is termed as physiologic mobilityThe reason for this mobility is that the tooth is not fused to the alveolar bone directly but is attached to the sockets by the periodontal ligament. Due to continued jaw growth and passive eruption of surrounding teeth ankylosed teeth will gradually appear to intrude.
It is greatest on arising in the morning progressively decreases. Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants. The main causes for traumatic injuries include accidents contact sports falls and violence.
Types Of Tooth Mobility. Tooth mobility should be determined using two single-ended instruments eg mouth mirror and probe. Tooth mobility was measured using the Periotest device at two timesafter removal of fixed appliance T1 and after bonding of the retainer T2.
Fixed reference point should be selected eg adjacent tooth that is not mobile and pressure should be applied in horizontal buccal-oral direction to the tooth we are testing. Physiologic tooth mobility 2. Download link is as follows.
Mobility is defined as the degree of looseness of the tooth. A free PowerPoint PPT presentation. Tronstad Andreasen Kristerson Clinically teeth lack physiologic mobility and exhibit a metallic tone on percussion.
PHYSIOLOGIC TOOTH MOVEMENT-ERUPTION AND SHEDDING - PHYSIOLOGIC TOOTH MOVEMENT ERUPTION AND SHEDDING 07-3121101-7008 7020 hosechkmuedu. This video is about How to assess TOOTH MOBILITYPdf notes available. It refers to a moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue.
Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants. In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years. Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Rev Belge Med Dent.
Grade 0 mobility Normal physiologic tooth mobility. Values of tooth mobility Periotest values were analysed between groups and compared with the physiologic tooth mobility in a control group of untreated patients n 65. Therefore determining tooth mobility gives useful information for the diagnosis and evaluation of the treatment outcome.
Replacement resorption occurs due to bony remodeling directly follows the resorptive process. Traumatic injuries to anterior teeth are one of the commonly faced problems faced by young children and adolescents. 1 Trauma incidence in permanent dentition is at its peak between 8 years and 10 years when children start engaging in different types of contact.
Measurement of tooth and implant mobility under physiological loading conditions In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years. Article in French Daniel A Aouizerat C Fournier B Brulin H Rassat P Praud J. All teeth have a slight degree of physiologic mobility which varies for different teeth at different times of the day.
Article in Dutch Author D vanSteenberghe. It refers to a moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue. This slight mobility is to bear masticatory forces on the teeth while chewing without harming themMilk primary teeth also become mobile.
Physiological tooth mobility seen in healthy teeth depends on the biophysical characteristics of the periodontal tissue whereas pathological tooth mobility is the result of the loss of periodontal support.

Treatment Of Tooth Mobility Smile Makeover Of La

Periodontal And Maintenance Complications Pocket Dentistry

Body Cavities And Membranes Medical School Studying Medical Anatomy Nursing School Studying

Figure 284a B Medical Massage Medical Anatomy Dental Assistant

Image From Http Www Mhhe Com Biosci Esp 2001 Saladin Folder Structure Su M3 S1 Assets Images Sum3s1 1 Jp Joints Anatomy Synovial Joint Anatomy And Physiology

Pin By Tejaswi Kothapally On Head And Neck Human Anatomy And Physiology Muscle Anatomy Muscular System

Orthodontic Tooth Movement The Biology And Clinical Implications Li 2018 The Kaohsiung Journal Of Medical Sciences Wiley Online Library

Baby Tooth Eruption Shedding Timeline Starting At 6 Months

Cmtautodom Gif 397 435 Pixels Teeth Diseases Neurology Cmt

Treatment Of Tooth Mobility Smile Makeover Of La





0 Response to "physiologic tooth mobility"
Post a Comment